Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have become essential tools in numerous industries, including construction and design.

GIS has changed the way architects and urban design professionals approach designing our cities, campuses, and urban environments. In architectural planning, GIS helps collect and analyse information about the urban context of a building site, including topography, infrastructure, and environmental factors. This data is crucial for making informed decisions during the design and construction process.
Types of GIS Technologies
GIS Software
GIS software platforms, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo, are essential tools for managing, analysing, and visualising geographic data. These software packages offer a wide range of capabilities, including data input, editing, analysis, mapping, and reporting.
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing technologies involve acquiring information about the Earth’s surface from a distance. This includes satellite imagery, aerial photography, and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging). Satellite imagery provides large-scale coverage of the Earth’s surface, while aerial photography offers higher resolution images of specific areas. LiDAR uses laser pulses to measure distances to the Earth’s surface, creating detailed 3D models of terrain and objects.
Global Positioning Systems (GPS)
GPS technology enables precise geolocation by receiving signals from satellites orbiting the Earth. GPS devices and receivers are used to determine the exact coordinates of a location, making them invaluable for field data collection, navigation, and mapping.
Field Data Collection Apps
Field data collection apps allow field crews to collect data directly in the field using mobile devices. These apps typically include features such as data entry forms, GPS location tracking, and photo and video capture. The collected data can then be synchronised with GIS databases for further analysis and visualisation.
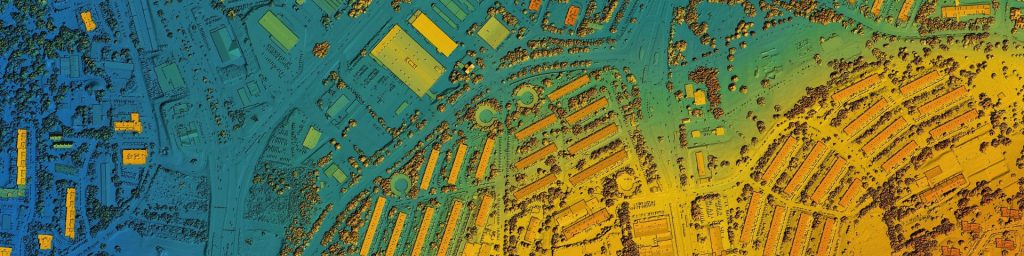
Key Applications of GIS in Architecture and Urban Design
1. Site Analysis and Selection:
Site analysis and selection involves evaluating a site’s suitability for development by considering factors such as topography, environmental impact, and accessibility. Topographic analysis helps assess site slope, aspect, and elevation, while environmental impact assessment identifies potential issues like noise pollution, air quality, and flooding. Accessibility analysis ensures equitable urban planning by considering proximity to transportation, amenities, and services. With GIS, architects can evaluate topography, climate conditions, land use, zoning regulations, and infrastructure, enabling a comprehensive understanding of the site. This technology allows for the integration of data layers to analyse environmental impact, accessibility, and potential constraints, ensuring sustainable and context-sensitive designs. By leveraging GIS, architects gain valuable insights that enhance planning efficiency and project outcomes.
2. Urban Planning and Design:
Land use planning involves creating detailed land use maps to optimise land use and minimise urban sprawl. Transportation planning focuses on designing efficient transportation networks, including roads, public transit, and pedestrian paths. Infrastructure planning involves planning the location and capacity of infrastructure, such as water supply, wastewater treatment, and energy distribution. With GIS, architects can analyse land use, infrastructure, population density, and environmental impacts to make data-driven decisions. Assisting in creating sustainable, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing urban layouts while addressing challenges like zoning regulations, traffic flow, and green space allocation.
3. Building Design and Construction:
Solar analysis helps determine the optimal building orientation and shading devices to maximise solar energy gain and minimise heat gain. 3D modelling creates accurate 3D models of buildings and urban environments for visualisation and analysis. GIS can help ensure that projects are delivered on time by tracking construction progress, identifying potential challenges, and optimising resource allocation also providing valuable insights into project feasibility and risk assessments.
4. Heritage Preservation and Conservation:
Heritage site mapping involves mapping and analysing heritage sites to inform conservation and restoration efforts. ArcGIS is a powerful and comprehensive GIS software suite that offers a wide range of tools for heritage analysis, mapping, and visualisation.
Remote Sensing technologies such as LiDAR Detection and Ranging, Satellite Imagery and Drone Imagery are all GIS software tools that help improve overall visualisation for architects by measuring or monitoring imagery and historical maps providing valuable data for further analysis. This allows architects to identify potential threats to heritage sites, enabling them to develop effective preservation and conservation strategies.

By embracing GIS technology, architects and urban designers can create more sustainable, resilient, and equitable cities and buildings.
If you enjoyed our article about For Architecture & Urban Design, take a look at our News section to see more.
Fewer Harrington & Partners is an Irish Architects Practice with offices in Waterford, Dublin and across the world.
Keep up with the latest updates by following us on LinkedIn. See our project portfolio here, or get in touch below:







